Here are my favorite and highest yield 31 medical mnemonics you should know in medical school. In medical school, people say weird things. In medical school, people say funny things. I GET PP SMASHED, PLAY TABLE TENNIS INSIDE PLAY TENNIS OUTSIDE, SOAP, SOAP, SOAP.
Why do we say these silly things? All of the above are memory aids. For example, I GET PP SMASHED, are possible causes of acute pancreatitis, PLAY TABLE TENNIS is about the clotting cascade and what helps you clot when you bleed, SOAP is how you present a new sick patient to the team you are working with.
Let’s get into it.
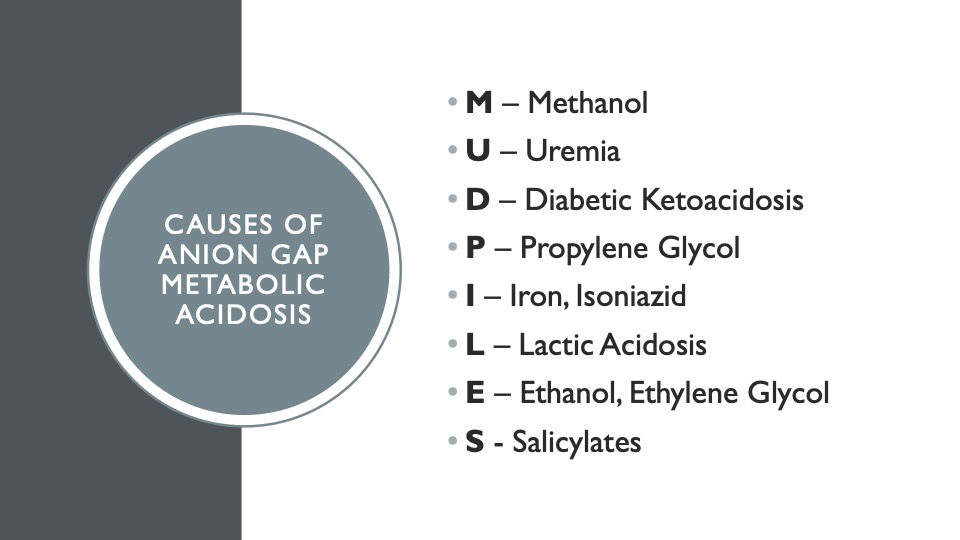
1. MUDPILES
Is this the most classic medical school mnemonic? I think so. Something in the body generates too much acid, which cannot be answered by looking at sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate levels. These are possible causes of anion gap metabolic acidosis.
2. OPQRST
A great way to think about pain is when someone comes to you complaining of pain. This is one of the first things I learned when I was an EMT, and I see attending physicians using it as well.

3. I GET PP SMASHED
A funny name that I will likely not forget. Here are some causes of pancreatitis. Alcohol is the most common cause, and gallstones are the second most common cause. Pancreatitis is when your pancreas is inflamed.

4. SIG E CAPS
Ways a physician might screen for depression. If any of these are positive, the physician should do a further look into possible depression.

5. DJI
I invented this one! This mnemonic is the only one I use consistently that I made up. Do you know DJI drones? When I was first learning about the human body, I wasn’t sure how to remember which came first the ileum, jejunum, or duodenum, all parts of the small intestine. This helped me remember it!

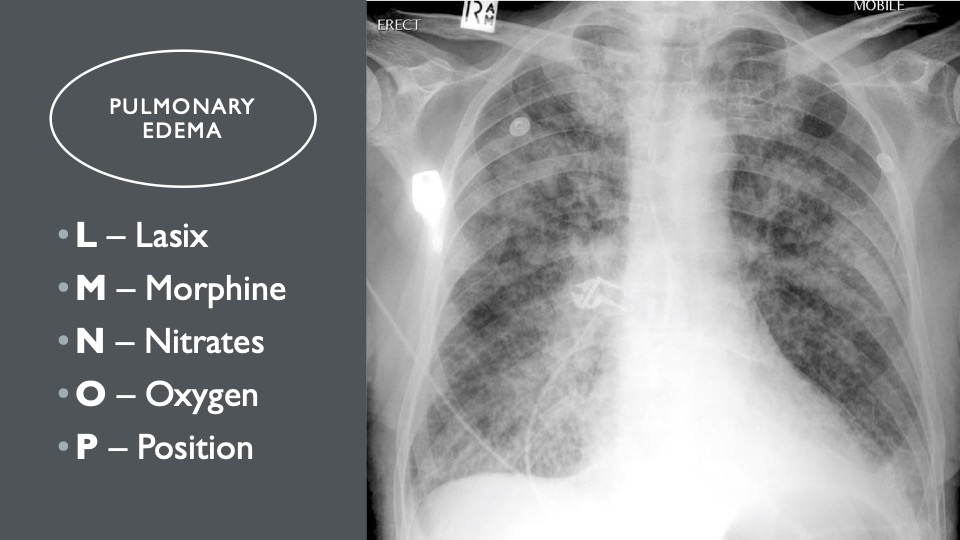
6. LMNOP
LMNOP is the treatment for pulmonary edema when there is too much fluid around your lungs.
7. SAD PERSONS
A helpful mental model, and actual scoring system, for assessing suicide risk in a person.

8. SOAP
I did not use this mnemonic at all in my first and second years of medical school. Now, in my third year, I use this every day. This is how I present every single one of my patients to my superiors.

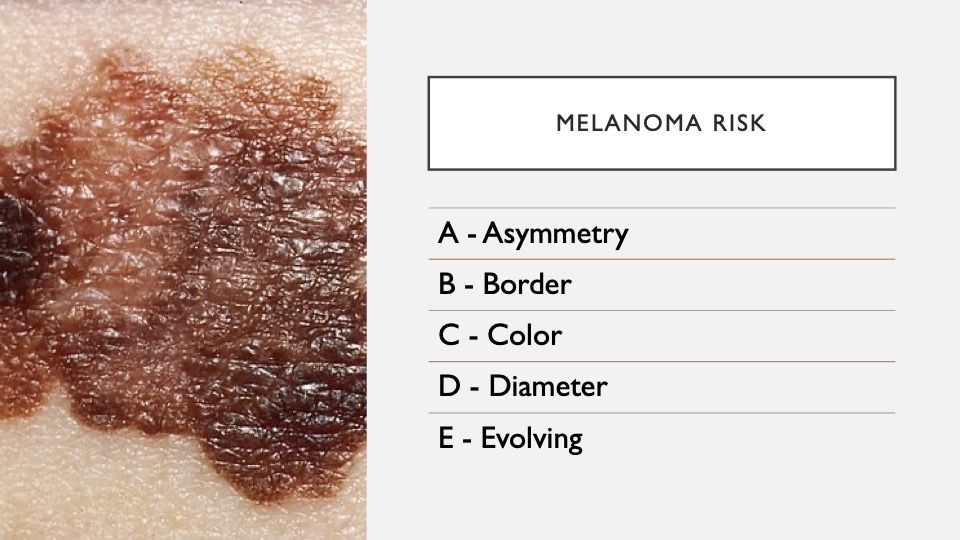
9. ABCDE
Common characteristics of melanoma to look out for.
10. PVT. TIM HALL
The essential amino acids. These are amino acids that the human body cannot make, so we must consume them.

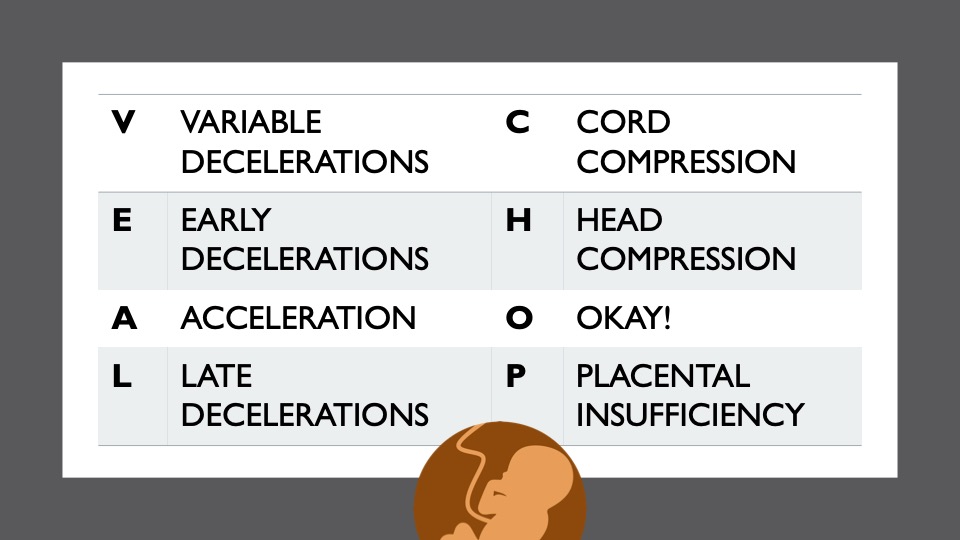
11. VEAL CHOP
A good mnemonic to relay the fetal heart rate and uterine contractions to what is actually going on with baby. The only one that is somewhat worrying is late decelerations.
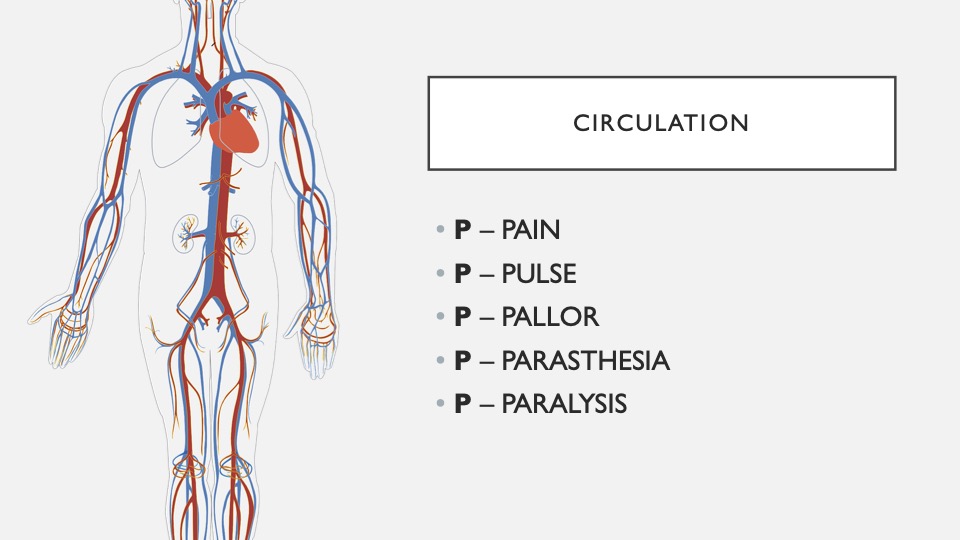
12. 5 Ps
A nice mnemonic to evaluate the circulation in an extremity.
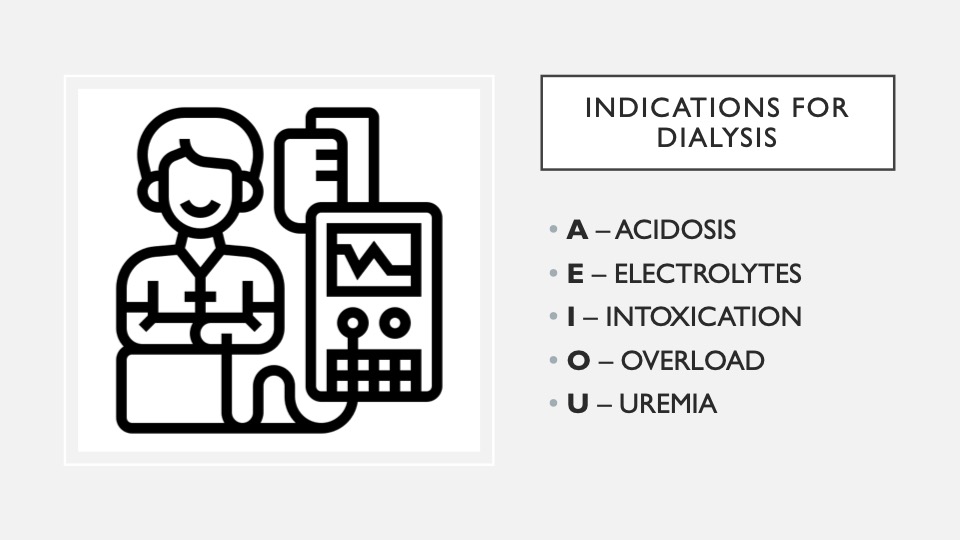
13. AEIOU
Indications for dialysis. AEIOU are indications for dialysis; when someone is so sick, we need to do what the kidneys usually do inside our body on the outside.
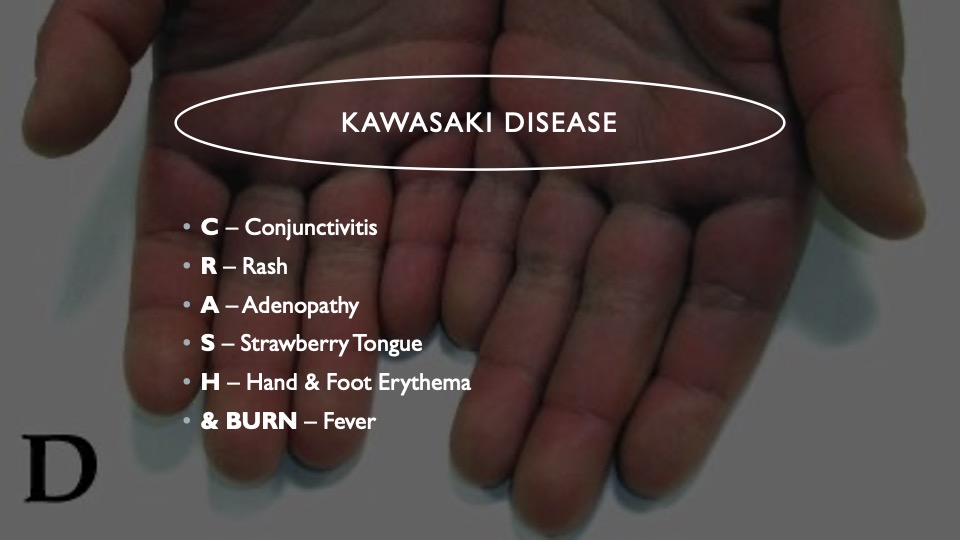
14. CRASH & BURN
Clinical signs of Kawasaki disease happen in young children, usually less than five, making children quite sick. It can sometimes even cause coronary heart disease in these young children, so identification is crucial to treat Kawasaki disease.
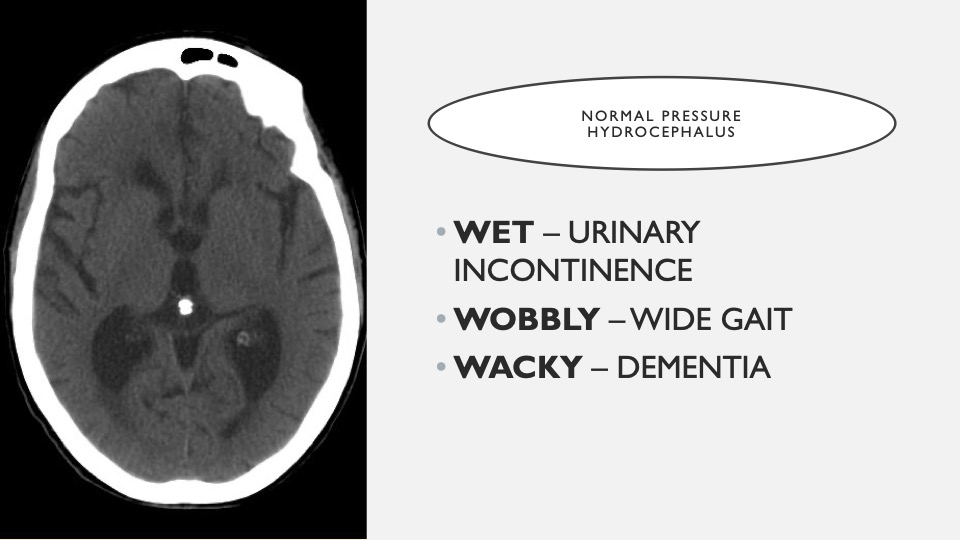
15. Wet Wobbly Wacky
Clinical signs of normal pressure hydrocephalus. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus is when excess fluid accumulates in the brain’s ventricles. The pressure, however, is strangely normal when you do a spinal tap and measure the pressure.
16. DIG FAST
These are the symptoms of a manic episode. A manic episode is characterized by a sustained period of abnormally elevated or irritable mood and the things described here. This often applies to people with bipolar disorder.

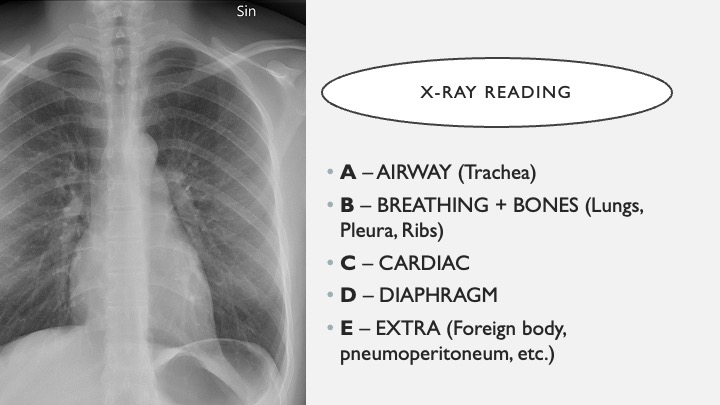
17. ABCDE X RAY
When I was first learning how to read X-rays, which I am still awful at, this was told to me and is an excellent way to start thinking about how to read an x-ray.
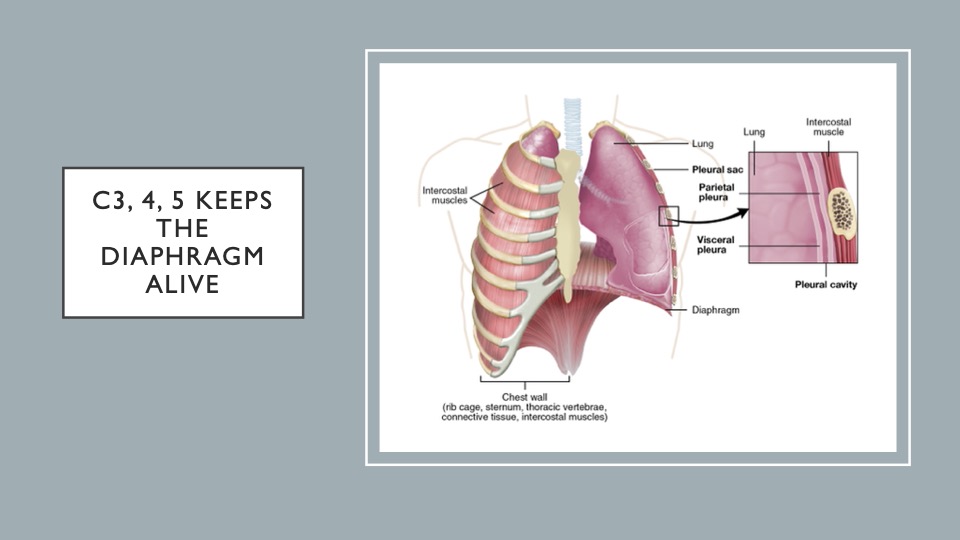
18. C3,4,5 KEEPS THE DIAPHGRAGM ALIVE
The phrenic nerve is a nerve that comes from the spinal roots C3, C4, C5, and it innervates various things, including the diaphragm. It’s a tool to remember which roots the phrenic nerve comes from and what innervates the diaphragm.
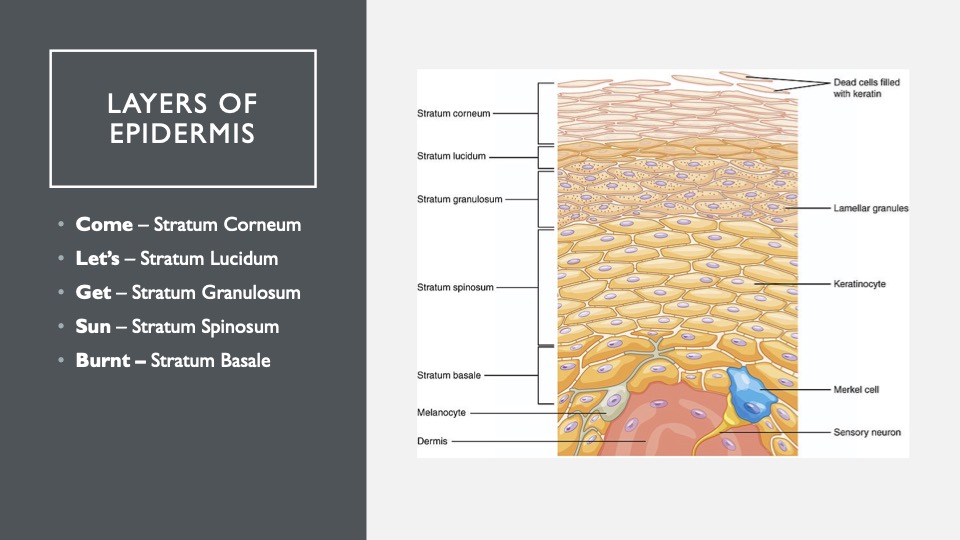
19. Come Let’s Get Sunburned
The layers of the epidermis, that top layer of skin we humans have.
20. FAT RN
Clinical presentation of Thrombotic (generates clots) Thrombocytopenic (low platelets) Purpura (tiny spots of bleeding seen on the skin). TTP is a possibly deadly condition, so identifying it early is essential.

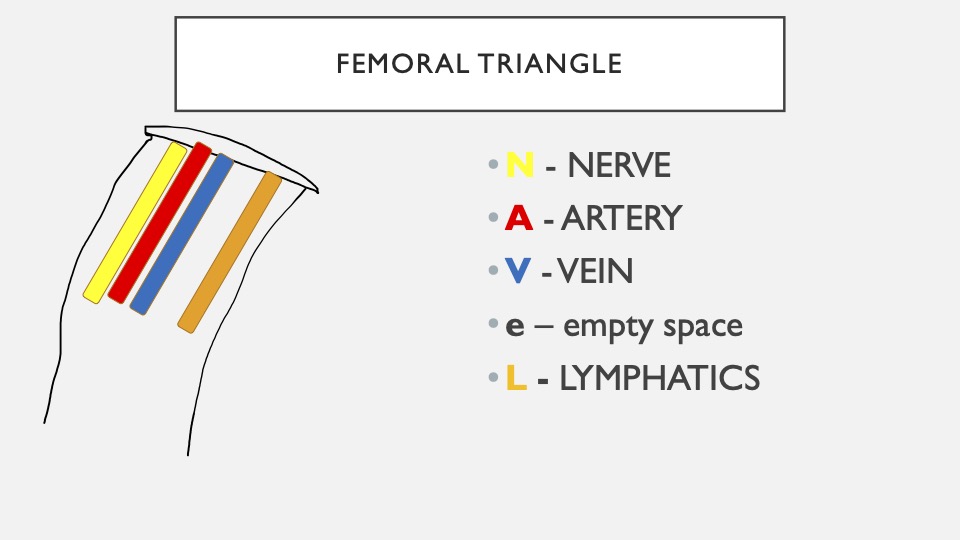
21. NAVEL
In your thigh, there is a femoral triangle that has a bunch of vital vessels. NAVeL is an excellent way to remember their order from outside (right of anterior thigh) to inside (left of anterior thigh).
22. I 8 10 EGGS AT 12
Another lovely anatomy memory technique to remember at what spinal cord level-specific structures are found. Inferior vena cava is the large vein that leads into the right side of the heart. The esophagus is what food goes down. The vagus nerve innervates the larynx and pharynx and has a vital role in swallowing, vocalization, and reducing heart rate. The aorta is the most significant artery in the body and takes oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.

23. ADEK
These are fat-soluble vitamins. It’s important to label these vitamins and remember them because, in certain diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, the intestines can’t absorb fats and, therefore, can’t absorb these vitamins.

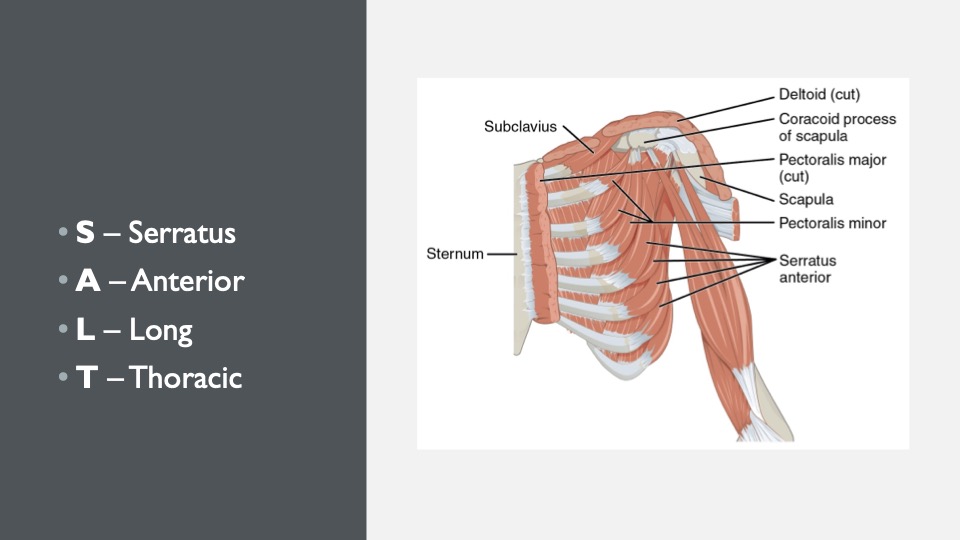
24. SALT
Anatomy mnemonic! Serratus anterior is innervated by the long thoracic nerve.
25. SPin SNout
Sensitivity and specificity took me forever to understand, and I still get confused sometimes, so don’t worry if this is confusing. Specificity is ruling something in if the test is positive. A highly specific test is a test, for example, testing for a disease, which is a test that is likely a true positive, meaning that if the test is positive, the person probably has the disease.
A sensitive test is ruling out if the test is negative. That means the test is likely to pick up the disease, but it might not be the only thing it picks up. So if a highly sensitive test is positive, you can not say, for sure, that the disease is there. You can say that the disease may be there. So if it’s a negative test, you can say it is likely that this person does not have this disease.
Confusing! I know, don’t worry about it. An understanding of it comes with time.

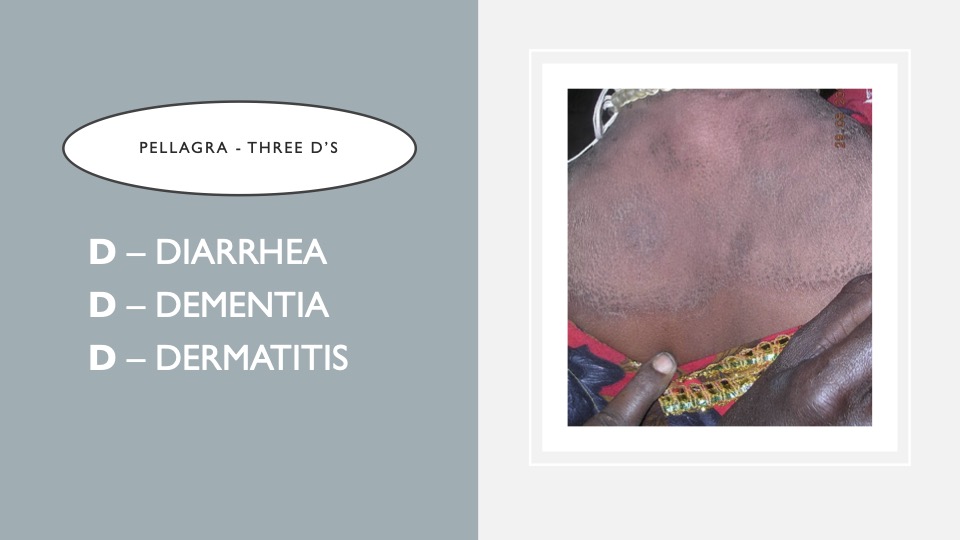
26. 3Ds Pellagra
When someone does not have enough Niacin, vitamin B3, they present with these symptoms.
27. Some Anatomists Like F****** Over Poor Medical Students
Branches of the external carotid artery, a longer one, but did help me a lot when I was trying to memorize the branches of this artery.

28. Carcinoid Syndrome Be FDR
Carcinoid syndrome if when a particular tumor, that is quite rare, that releases lots of serotonin. Lots of serotonin causes various manifestations in the body.

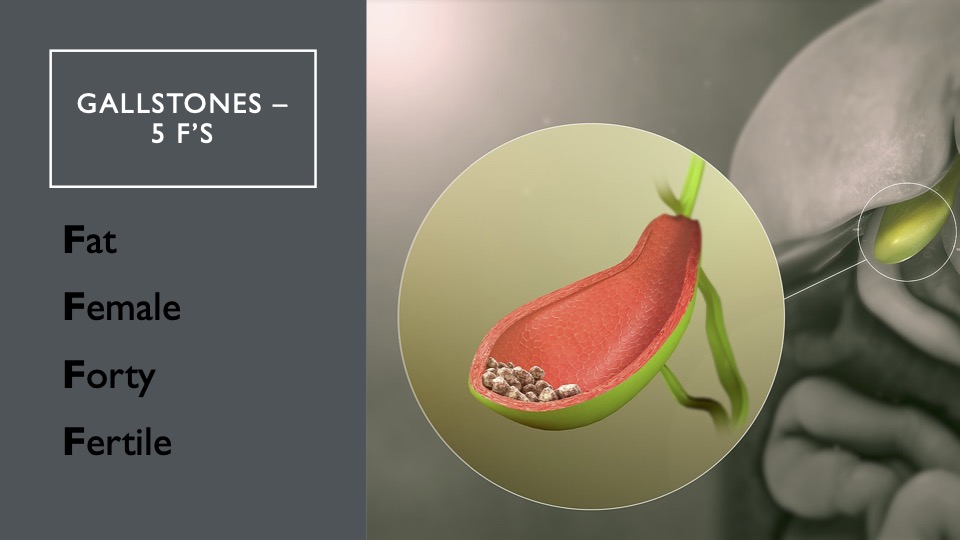
29. Gallstones, 4Fs Fat, Female, Forty, Fertile,
Certain people are more prone to gallstones. Gallstones are accumulations of certain things, usually bile, that accumulates in the gallbladder to such an extent that they actually form into a stone-like material.

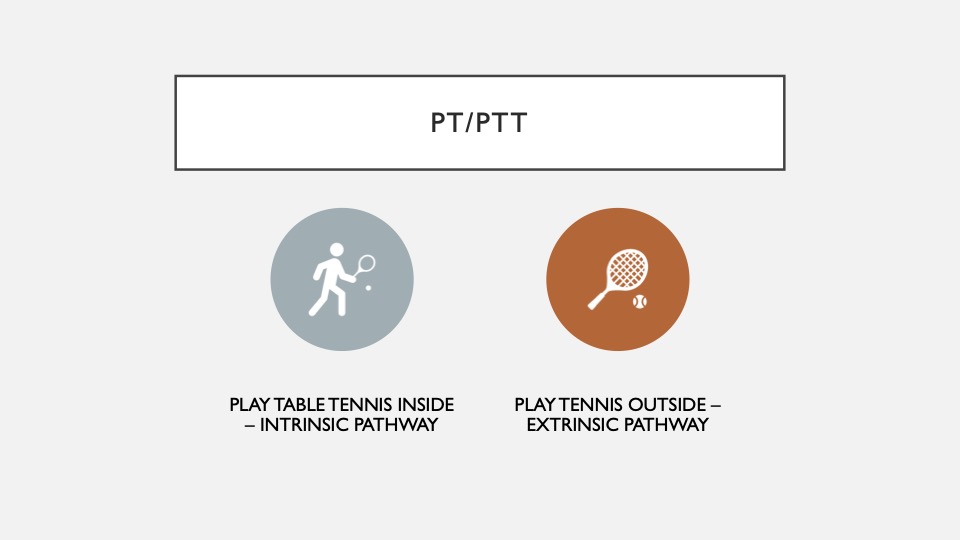
30. Play Table Tennis Inside, Play Tennis Outside
Someone told me this, and it stuck! When you bleed, your body has a specific strategy to clot. One is called the extrinsic pathway, which involves factor VII, and the other is called the intrinsic pathway, which requires factor XII, XI, IX, and VIII. The first stage of the clot is quick and doesn’t involve this pathway, the second stage, called the coagulation cascade, usually involves these pathways.
31. Some Say Money Matters But My Brother Says Big Boobs Matter More
Remembering all the cranial nerves is painful. Some have sensory functions. Some have motor functions. Some do both. This is an excellent way to remember which ones do which.

I hope you enjoyed these!
If you want a complete list, here is a great source (but too much for me to remember): http://www.medicalmnemonics.com/pdf/2002_09_full_abr_a4.pdf.
